Security and IT teams may be fresh off their holiday breaks, but threat actors have kept busy over the last month. In this edition of the Cybersecurity Threat Spotlight, we’re highlighting the Trojans, loaders, information stealers, and backdoors that we’re seeing online.
Want to learn more about how Cisco Umbrella can defend your enterprise against these threats? Request a personalized demo today!
Threat Name: Emotet
Threat Type: Trojan/Loader
Attack Chain:
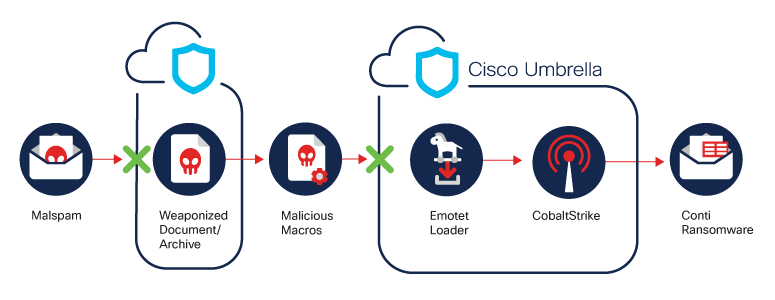
Description: Emotet is a banking Trojan that was first detected in 2014. Emotet has evolved into a massive botnet that delivers large amounts of malspam with malicious document attachments that lead to the Emotet Trojan. The Trojan also functions as a dropper for second-stage payloads, including – but not limited to – TrickBot, Qakbot, and Ryuk. Emotet has can steal SMTP credentials and email content. The threat actors reply to legitimate conversations in a victim’s email account, injecting replies that include malicious attachments.
Emotet Spotlight: In November, security researchers observed the return of the Emotet loader, which had been inactive since January 2021 after a law enforcement takedown. Emotet is a loader botnet that uses a Loader-as-a-Service model. Emotet’s main advantage is its modular system, which enables a highly targeted approach based on the requirements of the delivered payload. Unfortunately, the botnet has historically been leveraged by adversaries conducting sophisticated ransomware attacks.
At this point, security researchers observe strong connections between Emotet and Conti Ransomware. This can indicate that two cybercriminal syndicates are or will be establishing a new partnership. Historically, Conti was known to rely on sustainable methods of operation. Emotet has proven to be able to provide initial access and a strong foothold in multiple corporate networks. This can become the new trend in adversaries, and it will likely have a major impact on the threat landscape in 2022.
Target Geolocations: Worldwide
Target Data: User Credentials, Browser Data, Sensitive Information
Target Businesses: Any
Exploits: N/A
Mitre ATT&CK for Emotet
Initial Access:
Phishing: Spearphishing Attachment or Spearphishing Link, Valid Accounts: Local Accounts
Discovery:
Account Discovery
Process Discovery
Persistence:
Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys/Startup Folder
Create or Modify System Process: Windows Service
Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task
Execution:
Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell, Windows Command Shell, Visual Basic
User Execution: Malicious Link, Malicious File
Windows Management Instrumentation
Evasion:
Obfuscated Files or Information
Software Packing
Collection:
Archive Collected Data
Email Collection: Local Email Collection
Credential Access:
Brute Force: Password Guessing
Credentials From Password Stores: Credentials from Web Browsers
Network Sniffing
OS Credential Dumping: LSASS Memory
Unsecured Credentials: Credentials In Files
Command and Control:
Encrypted Channel: Asymmetric Cryptography, Non-Standard Port
Exfiltration:
Exfiltration Over C2 Channel
Lateral Movement:
Exploitation of Remote Services
Remote Services: SMB/Windows Admin Shares
Privilege Escalation:
Process Injection: Dynamic-Link Library Injection
IOCs:
Domains (Active)
cars-taxonomy[.]mywebartist[.]eu
crownadvertising[.]ca
giadinhviet[.]com
hpoglobalconsulting[.]com
immoinvest[.]com[.]br
itomsystem[.]in
pasionportufuturo[.]pe
thetrendskill[.]com
visteme[.]mx
cursossemana[.]com
callswayroofco[.]com
dipingwang[.]com
yougandan[.]com
Domains (Historical)
adorwelding[.]zmotpro[.]com
alfadandoinc[.]com
alfaofarms[.]com
av-quiz[.]tk
ceshidizhi[.]xyz
ckfoods[.]netdevanture[.]com[.]sg
evgeniys[.]ru
goodtech[.]cetxlabs[.]com
html[.]gugame[.]net
huskysb[.]com
im2020[.]vip
jamaateislami[.]com
laptopinpakistan[.]com
linebot[.]gugame[.]net
lpj917[.]com
manak[.]edunetfoundation[.]org
newsmag[.]danielolayinkas[.]com
onlinemanager[.]site
parentingkiss[.]com
pibita[.]net
primtalent[.]com
protracologistics[.]com
ranvipclub[.]net
ridcyf[.]com
server[.]zmotpro[.]com
staviancjs[.]com
team[.]stagingapps[.]xyz
thepilatesstudionj[.]com
vcilimitado[.]com
vegandietary[.]com
voltaicplasma[.]com
www[.]168801[.]xyz
www[.]caboturnup[.]com
xanthelasmaremoval[.]com
yoho[.]love
IPs (Active)
151[.]80[.]142[.]33
87 [.] 248 [.] 77 [.] 159
159 [.] 65 [.] 76 [.] 245
IPs (Historical)
105[.]247[.]100[.]215
118[.]244[.]214[.]210
120[.]150[.]206[.]156
12[.]57[.]239[.]19
139[.]162[.]157[.]8
139[.]59[.]242[.]76
169[.]64[.]242[.]153
173[.]90[.]152[.]220
179[.]52[.]236[.]96
181[.]119[.]30[.]35
181[.]229[.]155[.]11
185[.]129[.]3[.]211
185[.]97[.]32[.]6
186[.]176[.]182[.]192
186[.]4[.]234[.]27
189[.]130[.]50[.]85
189[.]234[.]165[.]149
190[.]128[.]27[.]233
200[.]27[.]55[.]100
200[.]56[.]104[.]44
208[.]180[.]149[.]228
208[.]180[.]246[.]147
216[.]176[.]21[.]143
216[.]251[.]1[.]1
23[.]254[.]203[.]51
24[.]206[.]17[.]102
37[.]120[.]175[.]15
45[.]123[.]3[.]54
50[.]100[.]215[.]149
50[.]125[.]99[.]70
51[.]75[.]168[.]89
54[.]39[.]176[.]22
54[.]39[.]181[.]130
67[.]215[.]49[.]234
67[.]43[.]253[.]189
86[.]98[.]71[.]86
92[.]207[.]145[.]74
96[.]246[.]206[.]16
Additional Information:
Back from the dead: Emotet re-emerges, begins rebuilding to wrap up 2021
Corporate Loader “Emotet”: History of “X” Project Return for Ransomware
Which Cisco Products Can Block:
Cisco Secure Endpoint
Cisco Secure Email
Cisco Secure Firewall/Secure IPS
Cisco Secure Malware Analytics
Cisco Umbrella
Cisco Secure Web Appliance
Threat Name: RedLine Stealer
Threat Type: Information Stealer
Attack Chain:
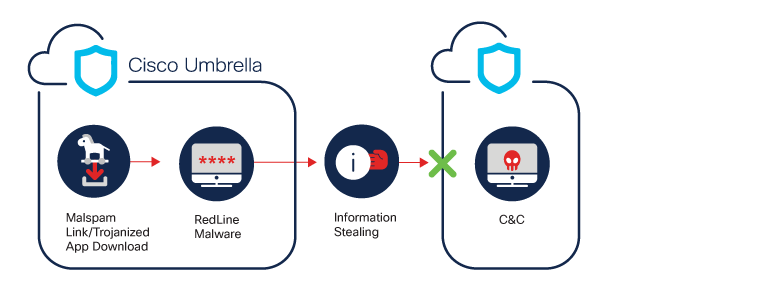
Description: RedLine is an information stealer available as a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) on Russian underground forums. It steals information like login credentials, autocomplete fields, passwords, and credit card information from browsers. It also collects information about the user and their system, like the username, location, hardware configuration, and installed security software. Finally, a recent update to RedLine also adds the ability to stead cryptocurrency cold wallets. RedLine appears to be under active development, with frequent introductions of new features.
RedLine Spotlight: Security researchers discovered that most stolen credentials currently sold on the dark web underground markets had been collected using RedLine Stealer malware. RedLine Stealer attempts to harvest information from browsers – like passwords, cryptocurrency wallets, and VPN services – and system information – like hardware configuration and location. Over the past year, RedLine has been enhanced with the addition of new features. It is now capable of loading other malware software and running commands while periodically sending updates containing new information from the infected host to its C2. The main goal of cybercrime campaigns utilizing RedLine Stealer appears to be the sale of stolen data to other cybercriminals who weaponize it in their own attacks.
Target Geolocations: Any
Target Data: User Credentials, Browser Data, Financial and Personal Information, Cryptocurrency Wallets
Target Businesses: Any
Exploits: N/A
MITRE ATT&CK for RedLine
Initial Access:
Phishing
Trojanized Applications
Credential Access:
Credentials from Password Stores
Steal Web Session Cookie
Unsecured Credentials
Credentials from Password Stores: Credentials from Web Browsers
Discovery:
Account Discovery
Software Discovery
Process Discovery
System Time Discovery
System Service Discovery
System Location Discovery
Peripheral Device Discovery
Persistence:
Registry Run Keys/Startup Folder
Scheduled Task/Job: Scheduled Task
Execution:
User Execution
Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell
Evasion:
Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify Tools
Collection:
Screen Capture
Command and Control:
Non-Standard Port
Non-Application Layer Protocol
Exfiltration:
Exfiltration Over C2 Channel
IOCs
Domains (Historical)
userauto[.]space
22231jssdszs[.]fun
hssubnsx[.]xyz
dshdh377dsj[.]fun
IPs (Active)
185[.]215[.]113[.]114
IPs (Historical)
37[.]0[.]8[.]88
193[].142[.]59[.]119
136[.]144[.]41[.]201
Additional Information
RedLine Stealer identified as primary source of stolen credentials on two dark web markets
Redline Stealer
Shining a Light on RedLine Stealer Malware and Identity Data Found in Criminal Shops
Which Cisco Products Can Block:
Cisco Secure Endpoint
Cisco Secure Email
Cisco Secure Firewall/Secure IPS
Cisco Secure Malware Analytics
Cisco Umbrella
Cisco Secure Web Appliance
Threat Name: Magnat Backdoor
Threat Type: BackDoor
Attack Chain:[1]

Description: Magnat BackDoor is an AutoIt-based installer that prepares a system for remote Microsoft Desktop Access and forwards the RDP service port on an outbound SSH tunnel. This installer’s actions pave the way for the attacker to access the system remotely via RDP. The malware applies this technique by setting up a scheduled task that periodically contacts a C2 server and sets up the tunnel if instructed by the C2 response.
Magnat BackDoor Spotlight: Cisco Talos recently observed a malicious campaign offering fake installers of popular software as bait to get users to execute the malware on their systems. This campaign includes a set of malware distribution campaigns that started in late 2018 and have targeted Canada, the U.S., Australia, and some European Union countries. Two undocumented malware families (a BackDoor and a Google Chrome extension) are consistently delivered together in these campaigns. An unknown actor with the alias “magnat” is likely the author of these new families and has consistently developed and improved them. The attacker’s motivations appear to be financial gain from selling stolen credentials, executing fraudulent transactions, and providing Remote Desktop Access to systems.
Target Geolocations: Canada, U.S., Australia, E.U. Countries
Target Data: Credentials, Sensitive Data
Target Businesses: Any
MITRE ATT&ACK for Magnat BackDoor
Initial Access:
Malvertising
Persistence:
Scheduled Task/Job
Execution:
Scheduled Task/Job
Evasion:
Impair Defenses: Disable or Modify System Firewall
Deobfuscate/Decode Files or Information
Command and Control:
Application Layer Protocol
Exfiltration:
Exfiltration Over Command and Control Channel
IOCs
Domains (Active)
chocolatepuma[.]casa
wormbrainteam[.]club
430lodsfb[.]xyz
softstatistic[.]xyz
happyheadshot[.]club
aaabasick[.]fun
nnyearhappy[.]club
teambrainworm[.]club
yanevinovat[.]club
fartoviypapamojetvse[.]club
hugecarspro[.]space
burstyourbubble[.]icu
boogieboom[.]host
cgi-lineup[.]website
newdawnera[.]fun
bhajhhsy6[.]site
iisnbnd7723hj[.]digital
sdcdsujnd555w[.]digital
Additional Information:
Which Cisco Products Can Block:
Cisco Secure Endpoint
Cisco Secure Firewall/Secure IPS
Cisco Secure Malware Analytics
Cisco Umbrella
[1] While Cisco products can protect against RDP BackDoor and Information Stealer, they do not protect against Chrome Extension Installers
