With economies on lifelines and work being done by teleconference calls, it may seem sometimes like the whole world is on hiatus. But the reality is that cyberattackers aren’t sleeping. Their tactics and targets may be shifting and changing, but the threats are not going away.
Key Highlights
In the first half of 2020, Cisco Umbrella identified the following threat trends:
- an evolution in repurposing trojans and droppers for new forms of malware delivery
- an increase in obfuscation and the use of macros and other fileless* malware to evade traditional antivirus (A/V) defenses
- a rise in threats to managed service providers (MSPs)
- loads of phishing tactics with COVID-19 related themes (which comes as no surprise – learn more about this in our earlier blog post).
Cisco Umbrella global network
Before we dig into the data, it’s helpful to remind ourselves how the Cisco global network views the threat landscape. Our 32+ customer facing data centers process 220+ billion domain naming service (DNS) requests daily. This gives us a unique perspective on global DNS traffic. This analysis is based on aggregated DNS query logs paired with scrubbed and anonymized customer demographic information.
Cisco Umbrella protects against more than 7 million malicious domains and IPs, while discovering over 60,000 new malicious destinations (domains, IPs, and URLs) on a daily basis. Each node of attack infrastructure is an opportunity to identify and neutralize before it can be used for new attacks. Cisco believes it’s better to predict and prevent cyberattacks.

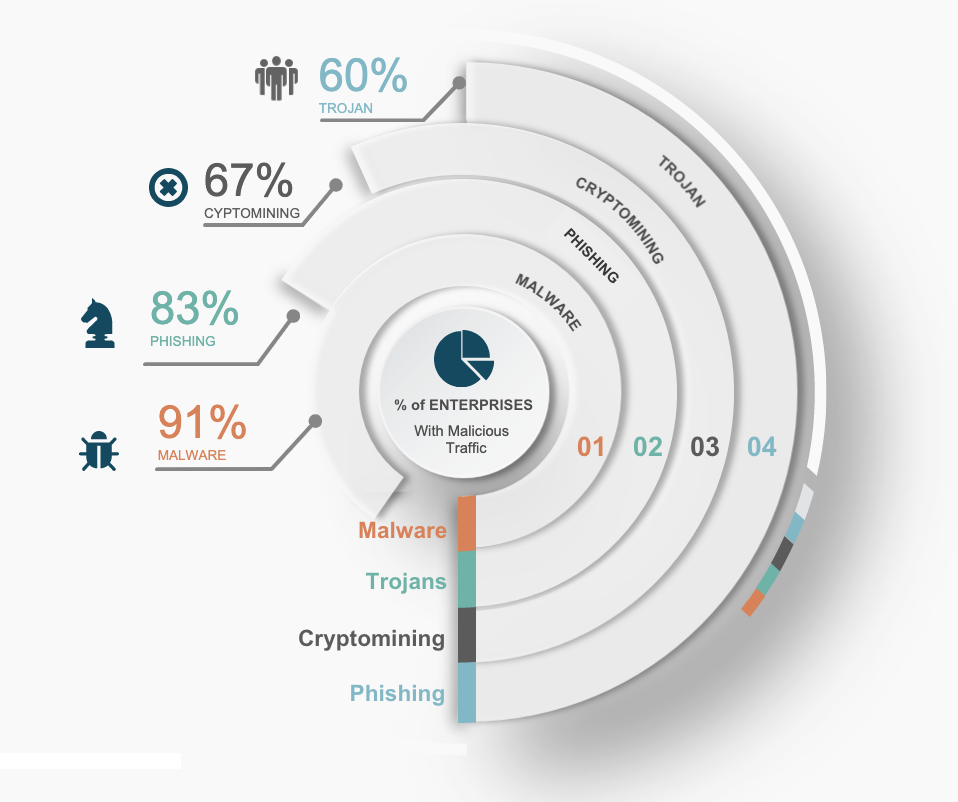
Phishing moved into second place behind malware in the first half of 2020
Looking at our entire customer base in the first half of 2020: 91% of them saw a domain linked to malware, 83% of them saw a domain linked to phishing, 67% of them saw a domain linked to cryptomining, and 60% of them saw a domain linked to trojans. Last year, trojans were the second most active at 59% and phishing was in the fourth spot at 46% impacted. One of the reasons for the shift this year was due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the huge increase in malicious phishing sites preying on peoples’ fears around the virus.
Top attacks impacting Umbrella customers:

Looking at the top attacks we’ve seen so far in 2020, it’s not surprising that cryptomining takes the top spot. Cryptomining was also the #1 attack last year by query volume. We saw more cryptomining in 2019 than in 2020, but the reduction in crypto query volume in 2020 wasn’t enough to drop cryptomining from the #1 spot.
However, it is important to note that cryptomining is inherently chattier than these other attacks, so its strong lead over these other top attacks is not as pronounced as it appears in terms of DNS query volume.
Trend #1: A new form of malware delivery
We’re seeing an evolution in repurposing trojans and droppers for new forms of malware delivery. Emotet comes in at #2. It started as a successful banking trojan, but quickly evolved into an even more successful delivery vehicle for malware dropping. Attackers are clearly sticking with what works. With its sophisticated modular architecture, worm-like propagation, and casting a wide net to impact the maximum number of victims – Emotet has become a workhorse for delivering numerous types of malware.
Ursnif/Gozi is another example of a trojan/dropper that is evolving its use cases. This attack type is being spread as a standalone version and as a dropper for other malware. It leverages email thread hijacking and abuse of trusted services such as Google Drive. Its targeted approach to the choice of delivery method depending on potential victims has made it popular in a wide variety of attacks.
Trend #2: Complexity, macros and fileless malware on the rise
Perhaps one of the biggest trends we have continued to see in the first half of 2020 has been the rise of more complex, multi-staged attacks. These attacks use new delivery mechanisms such as macros and other legitimate application functionality to evade A/V detection, obfuscation of data exfiltration (e.g., steganography), and coordination through command-and-control (C2) infrastructure.

For example, the above attack chain illustrates how malspam delivers an innocent-looking document that uses a macro or PowerShell (functionality embedded into the application used to open the file). This then leads to a payload/dropper that disables security controls, establishes persistence, and downloads additional malware. When all of the targeted data is exfiltrated, TrickBot is downloaded and launched. TrickBot processes take control of the domain controller via SMB Exploit which leads to network compromise. The last step in the infection chain is ransomware, which encrypts all affected components.
A variant on the data exfiltration step may be to use steganography. Steganography is the art of concealing information inside pictures. Attackers have used this technique specifically during this pandemic phase to exfiltrate data using steganography and is part of legitimate traffic.
Similarly, in the phase where the file employs some fileless automation such as Macros 4.0, VBA or PowerShell, the attack can make use of the legitimate software automation to obfuscate and then deobfuscate commands. Following is an example for a Macros 4.0 exploit using a Binary Interchangeable File Format (BIFF), which hides an embedded Microsoft Excel file.

The download happens from the attackers’ infrastructure, which apparently is a series of compromised WordPress sites. Attackers are constantly running a parallel campaign throughout the year in targeting small/medium businesses WordPress sites and adding it to their compromised kitty of domains. These domains are loaded within the Excel files, so that when de-obfuscation happens, it ends up downloading the actual .exe malware from compromised WordPress domains.
Trend #3: A new favorite target – managed service providers (MSPs)
Threat Traffic by Industry Vertical:
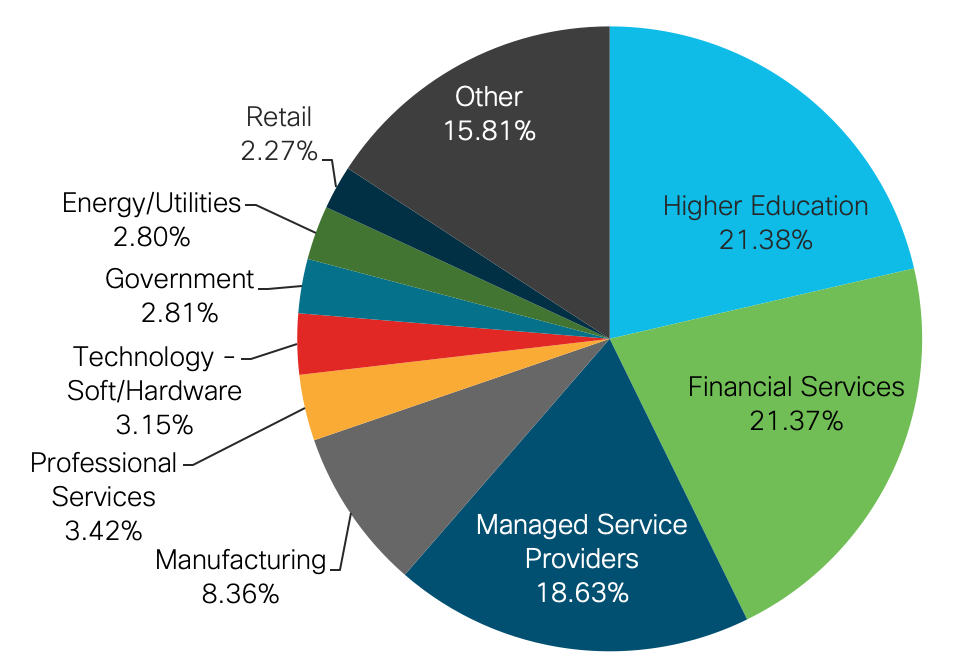

The distribution of threat traffic by vertical has changed slightly from its distribution in 2019. Managed service providers at 28.47% has overtaken financial services at 23.49% for the top spot of most impacted vertical. Higher education traffic has fallen considerably in its share of the pie from the #2 spot to #5. This considerable drop in higher education threat traffic is most likely the result of students not being present in person for classes.
Trend #4: COVID click bait drives increase in phishing
The COVID-19 pandemic has a lot of people on edge. Many of us are paying closer attention to emails and article headlines offering up COVID-19 stats in our area or where to go to get free testing. Malicious actors have taken advantage of our interest in the topic and set up numerous sites to phish for credentials and drop malware.
The largest jump in malicious COVID-19 query traffic in North America was 6.3X and occurred from the beginning of February through the end of June.
The largest jump in malicious COVID-19 query traffic outside of North America was 13.2X in the period from the beginning of March through the end of May.
2020 – the year that keeps on giving
The first half of 2020 has been eventful with the rise of COVID-19 and the widespread move to remote work for much of the global workforce. The landscape has changed — more considerably for some sectors than others — but the bottom line is that malicious actors are still working hard to infiltrate your environment. A “little” pandemic will slow them down, but not stop them.
Thanks to Shyam Sundar Ramaswami for contributing the malware sample analysis.
About Cisco Umbrella
Cisco Umbrella delivers the most secure, reliable, and fastest internet experience to more than 100 million business and consumer users daily. Umbrella unifies firewall, secure web gateway, DNS-layer security cloud access security broker (CASB), and threat intelligence solutions into a single cloud service to help businesses of all sizes secure their network. As more organizations embrace direct internet access, Umbrella makes it easy to extend protection to roaming users and branch offices.
Leveraging insights from Cisco Talos, one of the world’s largest commercial threat intelligence teams with more than 300 researchers, Umbrella uncovers and blocks a broad spectrum of malicious domains, IPs, URLs, and files that are being used in attacks. We also feed huge volumes of global internet activity into a combination of statistical and machine learning models to identify new attacks being staged on the internet. Learn more about how we identify attacks with threat intelligence in this blog post from Chris Riviere.
In a recent test, Cisco Umbrella took the #1 spot in security efficacy against today’s threats. AV-TEST performed a review of Cisco cloud security solutions alongside comparable offerings from other vendors.
Learn more about how AV-TEST put our security to the test (and how we won). Read the report here.
* Fileless malware uses existing legitimate applications and system functionality to infiltrate a computer, leaving no signature and thereby evading traditional antivirus defenses. It typically functions by using legitimate tools for malicious purposes, such as LOLBins, and can include Microsoft Office Macros, PowerShell, among others.
